- Home
- Getting started
- Quick start guides
- Getting started with Expo projects
Getting started with Expo projects
Get started on Bitrise by signing up via email or a Git provider, connecting a repository, and running the first build for your Expo app.
You can generate React Native projects with the React Native CLI or with the Expo CLI. Expo is a toolchain that allows you to quickly get a React Native app up and running without having to use native code in Xcode or Android Studio.
In this guide we discuss how to set up, test, code sign and deploy your React Native project built with the Expo CLI.
Adding an Expo project to Bitrise
First, let’s see how to add a React Native Expo project to bitrise.io.
-
Log in to Bitrise and go to the Dashboard.
-
Click the New CI project button.
-
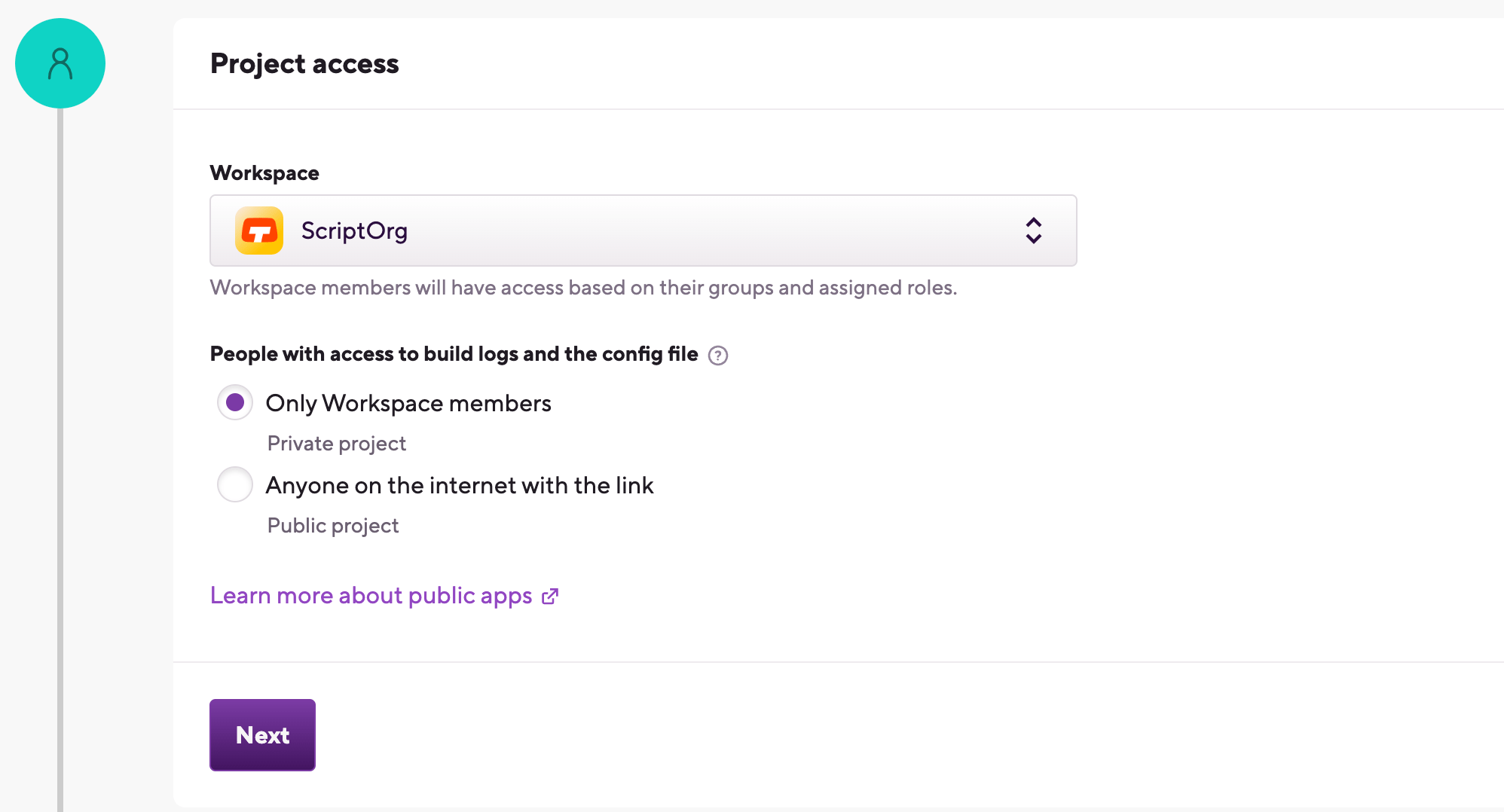
Under Project access, select the Workspace that will own the project.
-
Set the privacy of the project.
Privacy is final
You cannot change this setting later! If you realize you've accidentally added your project as a public project even though you need it to be private, you'll have to delete the project and add it again.
-
Private projects are only accessible to you, your Workspace members and those who are invited to work on a project. They require authentication to access the repository of the project.
-
Public projects expose their Configuration YAML and their build logs to everyone. If you have a public project’s build URL, you can view its build log, to help with troubleshooting, for example. Public projects do not require authentication and they cannot have SSH keys.
-
-
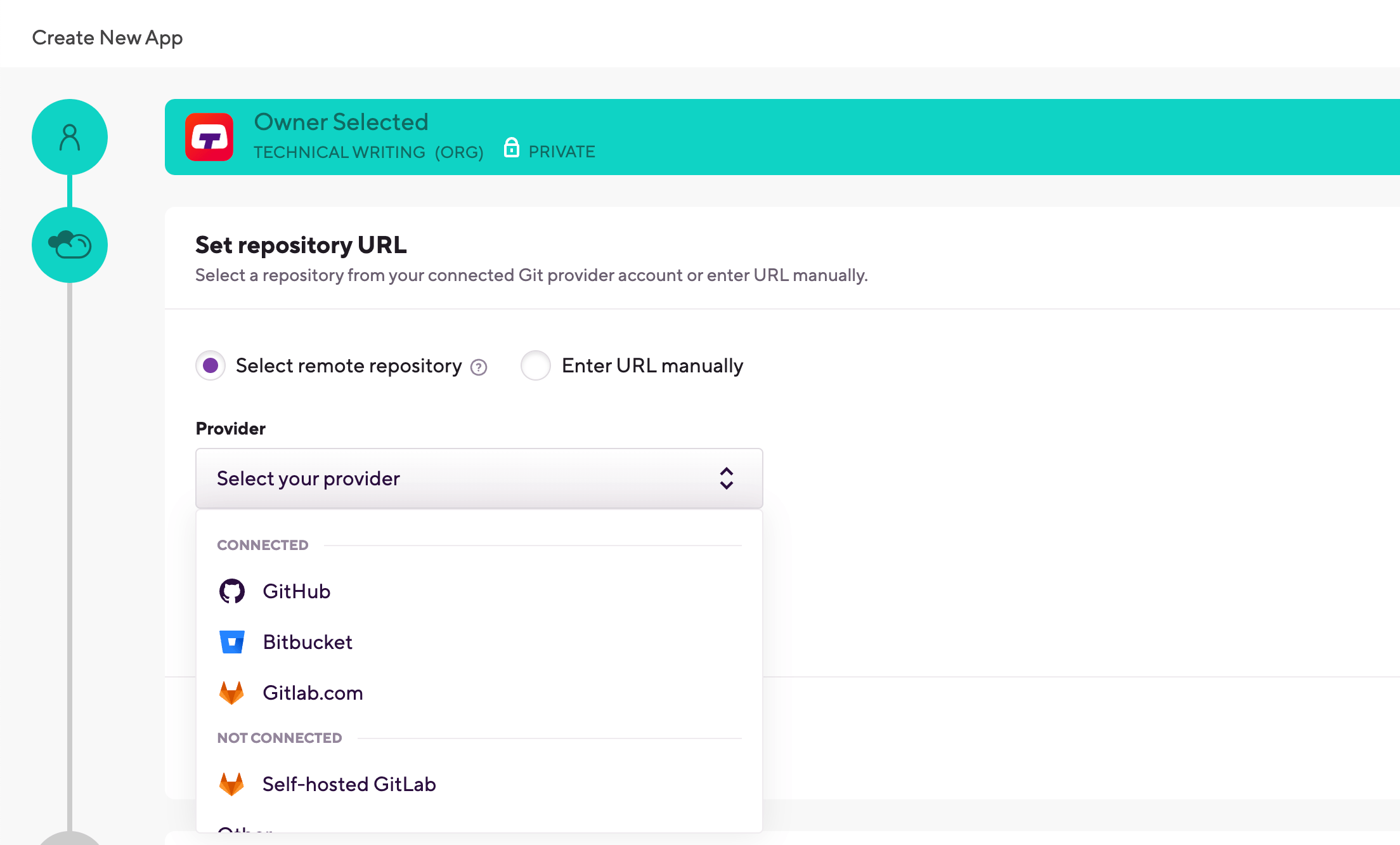
Select one of two options to set your repository URL:
-
With the Select remote repository option, you can select a repository from a list of repos from a connected Git provider account. Choose the Git provider from the dropdown menu, then click Select a repository... and select the repository from the list.
-
The Enter URL manually option does not require a connected Git provider account: you can simply enter the URL and proceed to the authentication phase. We strongly recommend using an SSH URL, unless you are setting up a public project.
Repository URL
You will be able to change your project's repository URL later. You can also connect or disconnect your account to Git provider services at any time.
If you signed up for Bitrise using a Git provider account, that one is already connected and you can select any of your repositories from it.
-
-
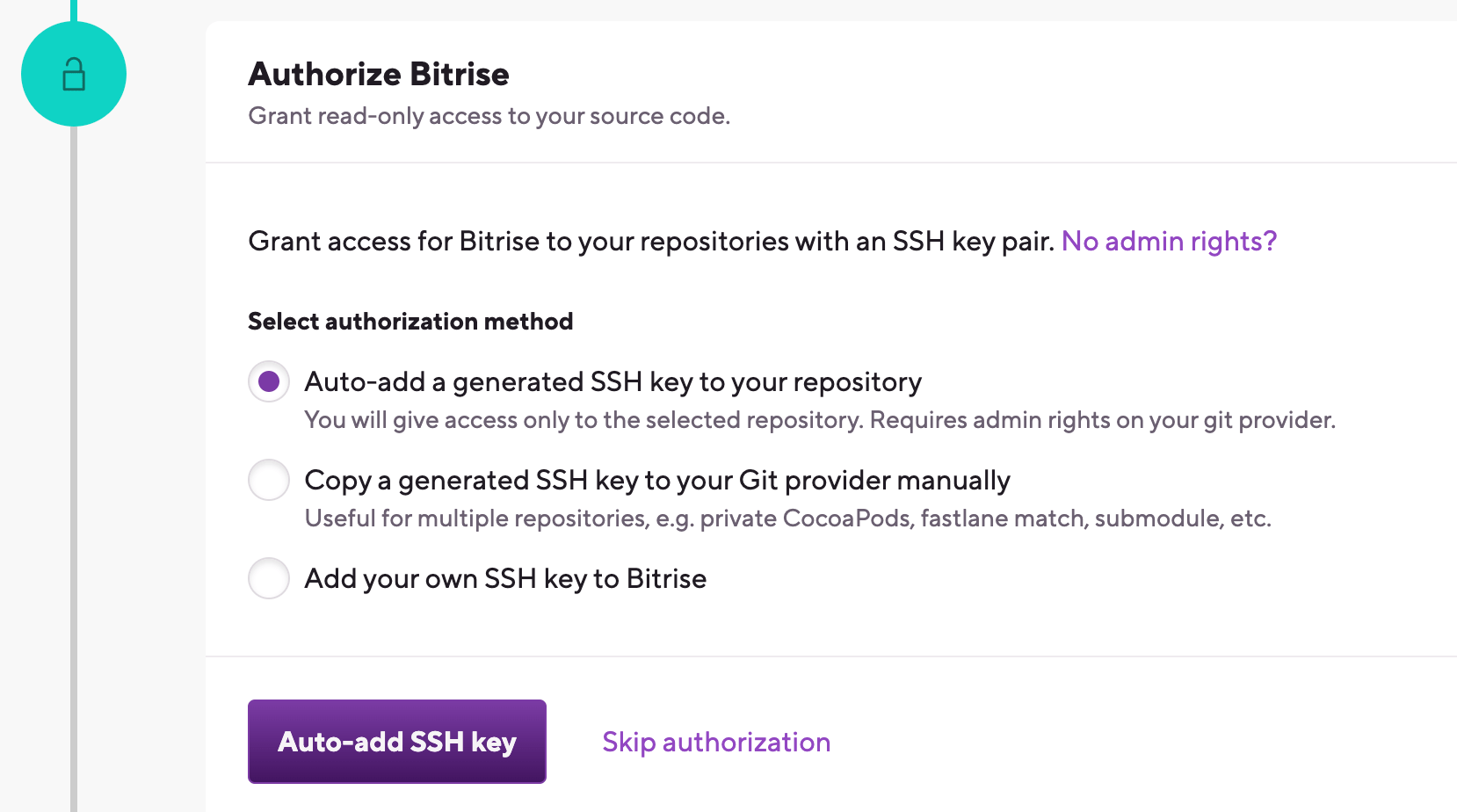
If you use an OAuth connection, you need to add an SSH key in the Authorize Bitrise section.
You don't need SSH keys if:
-
Your project is a public project.
-
You connect to your Git repository via a GitHub project installation.
-
Auto-add a generated SSH key to your repository: We recommend using this option. We automatically generate an SSH key pair and register the public key to your repository. Requires your connected Git provider account to have admin rights to the repository.
-
Copy a generated SSH key to your Git provider manually: We generate an SSH key pair for you and you can copy the public key and register it manually to your Git provider. It is useful if, for example, you need to access multiple repositories with the same SSH key.
-
Add your own SSH key to Bitrise: You can generate your own SSH key and paste the private key here after choosing this option. You also need to add the public key to the repository manually. To generate your SSH key pair: Generating your own SSH keypair.
Configure SSH keys at any time
If you can't set up a valid, working SSH key connection at this time, don't worry: proceed with adding your project. You can set up the SSH connection afterwards: Configuring SSH keys.
-
-
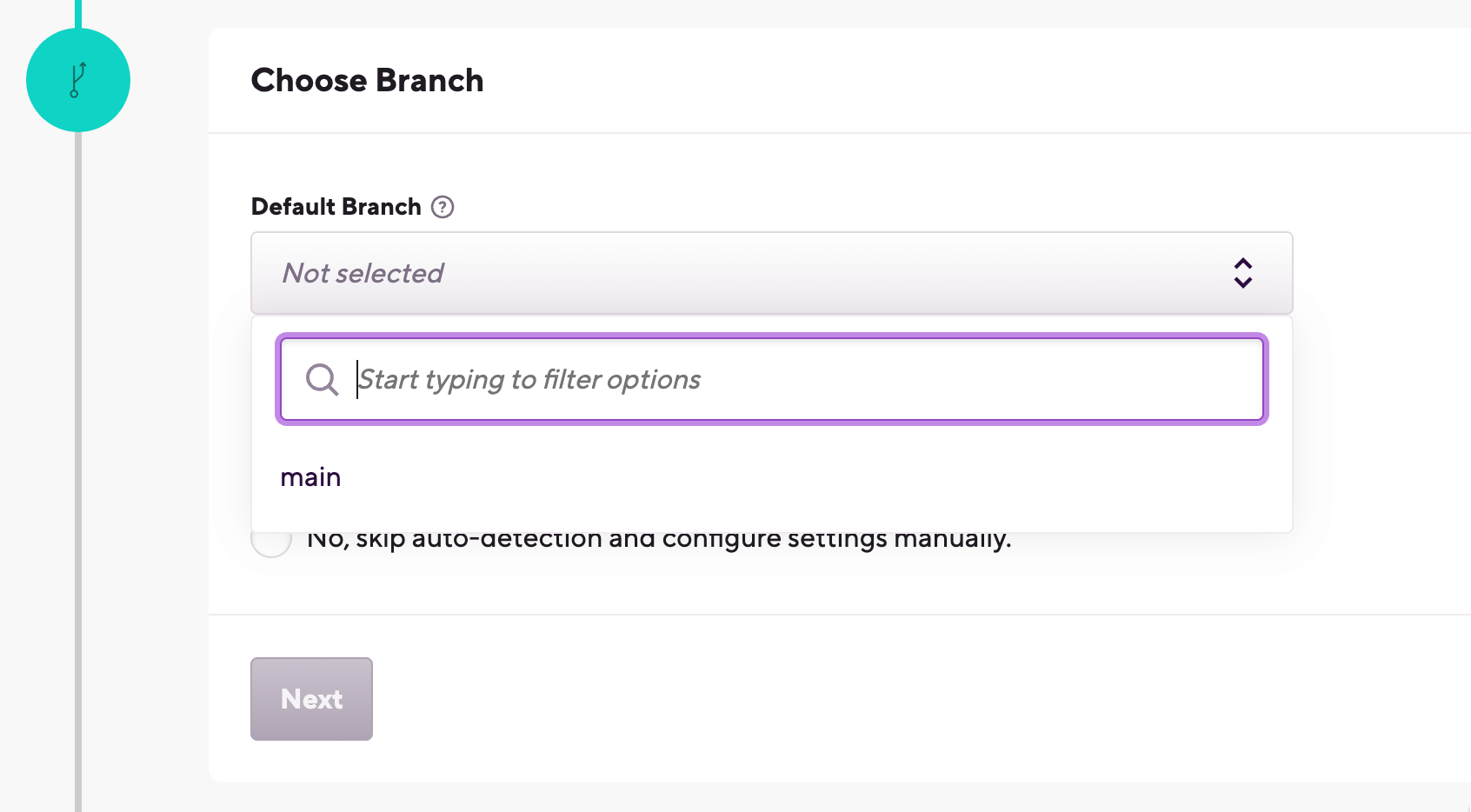
Select the default branch of your repository. This branch should contain the configuration of your project.
-
If you successfully configured SSH access in the previous step or if you're adding a public project, Bitrise will parse your repository and allow you to select a branch from a dropdown menu.
-
If you didn't configure repository access, you need to type the branch name manually.
You can change the default branch of the project later.
-
-
In the next step, choose Yes, auto-detect configuration. Bitrise will scan your repository and attempt to set up a stack and default Workflows based on the results of the scan. In most cases, we recommend choosing this option.
Project type
Detecting a project type serves to assist in the initial configuration of your project. But don't worry, you can change every setting, including the project type, at any time after you added the project.
-
Wait while Bitrise is validating your project. If automatic validation fails, you can set the project up manually.
-
Register a webhook when prompted so that Bitrise can start a build automatically when code is pushed to your repository, or a pull request is created.
-
Once you are done, click View Project Page to go to the newly added project's home page. From there, you can start editing your Workflows and run builds.
You have successfully set up your React Native project on bitrise.io! Your first build gets kicked off automatically using the primary workflow. You can check the generated reports of the first build on the Artifacts tab on your Build’s page.
Installing dependencies for Expo apps
If the Bitrise project scanner has successfully scanned your project, Run npm command or Run yarn command Steps will be included in your default Workflows. These Steps can install the missing Javascript dependencies for your app.
For native Android dependencies, you can use the Install missing Android SDK components Step.
For native iOS dependencies, you can use, among others, the Brew install Step or the Run CocoaPods install Step.
To install Javascript dependencies with npm:
Using Yarn instead of npm
In this guide, we're using npm to install Javascript dependencies. However, you can use the Run yarn command Step: it can install missing JS dependencies without any additional configuration required.
-
Log in to Bitrise and select Bitrise CI on the left, then select your project.
-
Click the Workflows button on the main page.
-
Make sure your Workflow includes the Run npm command Step.
-
In The 'npm' command with arguments to run input variable, type
install.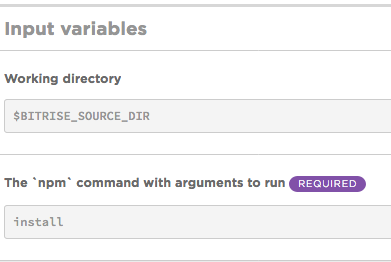
Using the
npm cicommand instead ofnpm installIf you already have an up to date
package-lock.jsonfile in your project, we recommend using thecicommand in The 'npm' command with arguments to run input. Usingnpm cican not only result in much faster build times compared tonpm installbut more reliable builds as well.
Testing your React Native app
You can use React Native’s built in testing method, called jest to perform unit tests.
-
Log in to Bitrise and select Bitrise CI on the left, then select your project.
-
Click the Workflows button on the main page.
-
Add the run npm command Step to your Workflow.
-
In the npm command with arguments to run input field, type
test.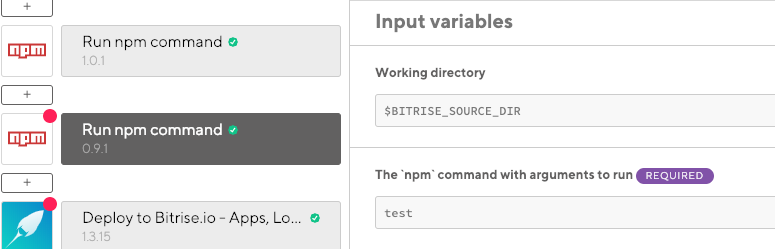
For more detailed guides on React Native testing, check out Testing React Native apps.
Adding React Native test results to Test reports
Bitrise's Test reports add-on allows you to view and analyze your test results in one convenient place. By default, these tests won't show up in Test reports. However, you can export the results: Exporting to Test Reports from any Step. The basic process is as follows:
-
Generate a
junit.xmlfile during the build.For example, you can use jest-junit to prepare a report.
-
Add the Export test results to the Test reports add-on Step to your Workflow.
-
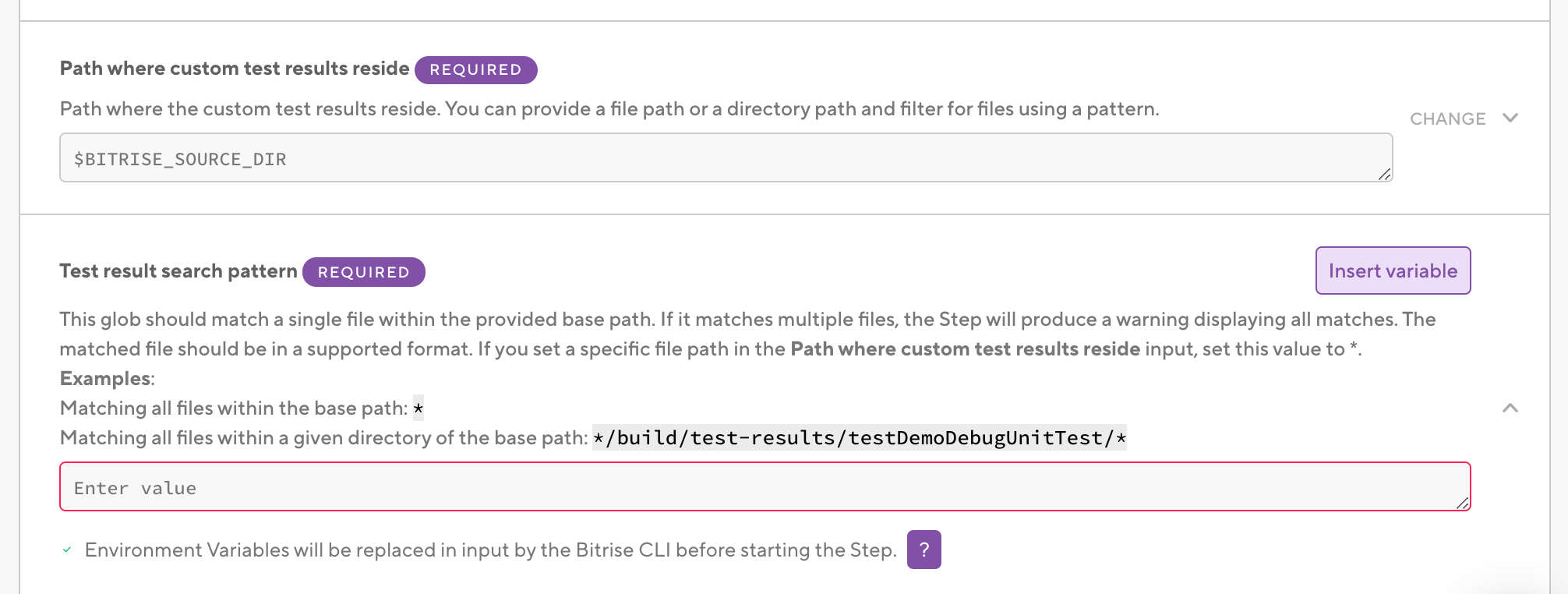
In the Path where custom test results reside input, add the folder in which your
junit.xmlfile and other test results are located. -
In the Test result search pattern input, set
*.xml. -
In the The name of the test input, set the name of the test run.
The test results will be under this name in the Test Reports add-on.
-
Make sure you have the Deploy to Bitrise.io Step in your Workflow.
Deploying your Expo project
Bitrise supports Expo Application Services (EAS) for Expo projects, and the default deploy Bitrise Workflow uses the Run Expo Application Services (EAS) build Step to trigger a build on EAS.
In case you don’t want to use EAS, you can use Turtle CLI for your Bitrise Workflows. See this Workflow Recipe for details.
A Step is a block of script execution that encapsulates a build task on Bitrise: the code to perform that task, the inputs and parameters you can define for the task, and the outputs the task generates.
A Workflow is a collection of Steps, Environment Variables, and other configurations. When Bitrise starts a build, it runs one or more Workflows according to the configuration defined in the bitrise.yml file.